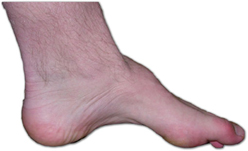
A pes cavus foot is a foot that has a very high arch. This foot type represents 8-15% of the world’s population, with 60% of this group experiencing chronic foot pain at some point in their life.
What causes a high arch?
 The cause of a pes cavus foot type is primarily caused by neurological diseases such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and cerebral palsy. Or it can be idiopathic, meaning a high arch is present but it is unknown why.
The cause of a pes cavus foot type is primarily caused by neurological diseases such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and cerebral palsy. Or it can be idiopathic, meaning a high arch is present but it is unknown why.
Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) is one of the most common neuromuscular diseases that can result in a pes cavus foot type. CMT is typically hereditary and is a result of a gene mutation. This disease is a progressive neurological condition effecting sensory and motor nerves, these are the nerves that control muscle function. Consequently, the nerve damage results in the inability to innervate muscles therefore, certain muscle groups weaken creating a muscle imbalance. This muscle imbalance results in tendons and muscles pulling on certain bones in the feet which can commonly result in a high arch.
Others causes can include:
- Traumatic injuries resulting in bone malformations
- Congenital club foot
- Laceration of a muscle on the side of your leg called the peroneus longus
What does this type of foot look like?
- High arches
- Clawed digits
- Callus formation on the lateral side of the foot of under the ball of the foot
- Stiff and rigid joints
How does this foot type function when walking?
The pes cavus foot functions differently depending on; the severity, if the joints in the foot are mobile or rigid, or if there is a neuromuscular disease associated with it. Common gait characteristics we see are:
- Walking on the outside of the foot
- Instead of toeing off through the big toe, toe off occurs through the little toes
- Instability when walking
- Based on the foot and ankles alignment there can be an increase of pressure on the inside of the knees.
- Pressure analysis show that there tends to be higher amount of pressure through the heel and front of the foot, with minimal contact going through the middle of the foot. However, research also shows that in a more progressive pes cavus foot (associated with neuromuscular disease) there will be higher amounts of pressure in the front of the foot as the muscle weakness can affect someone’s ability to strike with their heel when walking.
Injuries associated with a pes cavus foot type:
Literature illustrates that 60% of the population with a pes cavus foot type will experience chronic pain. Listed below are some of the most common conditions associated with a pes cavus foot type.
- Plantar fasciopathy (AKA plantar fasciitis)
- Pain under the ball of the foot
- Painful callus
- Achillies tendonitis
- Lateral ankle instability
- Stress fractures in the foot
- Knee pain
- impaired balance and stability
- Peroneal tendinopathy
- Fat pad atrophy
Management:
Customized orthotic management is shown to be the most effective management option for a pes cavus foot. Literature illustrates that foot pain scores increased by 74% with a customized orthotic, and function improved by 45%. Orthotic management is based individually depending on the level of foot dysfunction.
When the pes cavus foot has progressively worsened other treatment options in conjunction with an orthotic have clinically shown great results. This includes:
- Arizona brace
- Dictus band
- Shoe modifications
A pes cavus deformity associated with pain and dysfunction can affect quality of life, therefore it is important to manage it appropriately. Resonance Podiatrists are your specialists on biomechanical assessments, and can determine the necessary treatment/referral pathway needed.
References:
Barrie JL, McLoughlin C, Robem N, Nuttal R, Lishman J, Wardle F, Hopgood P. Ankle instability in pes cavus. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2001; 83-B: 339
Burns J, Crosbie J, Hunt A, Ouvrier R. The effect of pes cavus on foot pain and plantar pressure. Clinical Biomechanics 2005;20(9): 877–82.
Burns J. Redmond A. Ouvrier R. Crosbie J. Quantification of muscle strength and imbalance in neurogenic pes cavus, compared to health controls, using hand-held dynamometry. Foot & Ankle International. 26(7):540-4, 2005
Burns J. Crosbie J. Ouvrier R. Hunt A. Effective orthotic therapy for the painful cavus foot: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association. 96(3):205-11, 2006
Giannini S, Ceccarelli F, Benedetti MG, Faldini C, Grandi G. Surgical treatment of adult idiopathic cavus foot with plantar fasciotomy, naviculocuneiform arthrodesis, and cuboid osteotomy. A review of thirty-nine cases. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (American Volume) 2002;84-A(Suppl 2):62–9.
Williams DS, 3rd, McClay IS, Hamill J. Arch structure and injury patterns in runners. Clin Biomech 2001a; 16: 341-7
Korpelainen R, Orava S, Karpakka J, Siira P, Hulkko A. Risk factors for recurrent stress fractures in athletes. Am J Sports Med 2001; 29: 304-310
Make an Appointment to discuss further.

